General Ledger in Accounting Meaning, Examples,
A general ledger works by categorizing each financial transaction that occurs in the business. For every transaction, there is a corresponding debit and credit entry, which ensures the books are always balanced. Options to include on your GL chart of accounts are assets, liabilities, revenues, equities, and expenses, along with other income and expenses, if relevant. Your ledger will reflect the numbers that are important to your small business. You can prepare financial statements once you have verified the accuracy of your ledger accounts.
- After the journals are complete for the period, the account summaries are posted to the ledger.
- However, the business owner can easily find the total purchases amount from the purchases account.
- In addition to this, the information contained in general ledgers help you to run any audits smoothly.
- Batches or groups of similar accounts are kept together, and ledgers are indexed so that information pertaining to a particular account can be obtained quickly.
What is the difference between a general ledger and a journal?
The cost of sales is subtracted from that sum to yield the gross profit for that reporting period. For instance, cash activity is usually recorded in the cash receipts journal. The account details can then be posted to the cash subsidiary ledger for management to analyze before it gets posted to the general ledger for reporting purposes. Accounts receivable (AR) refers to money that is owed to a company by its customers. The accounts receivable process begins when a customer purchases goods or services from a company and is issued an invoice. The customer usually has a set amount of time to pay the invoice, such as 30 days.
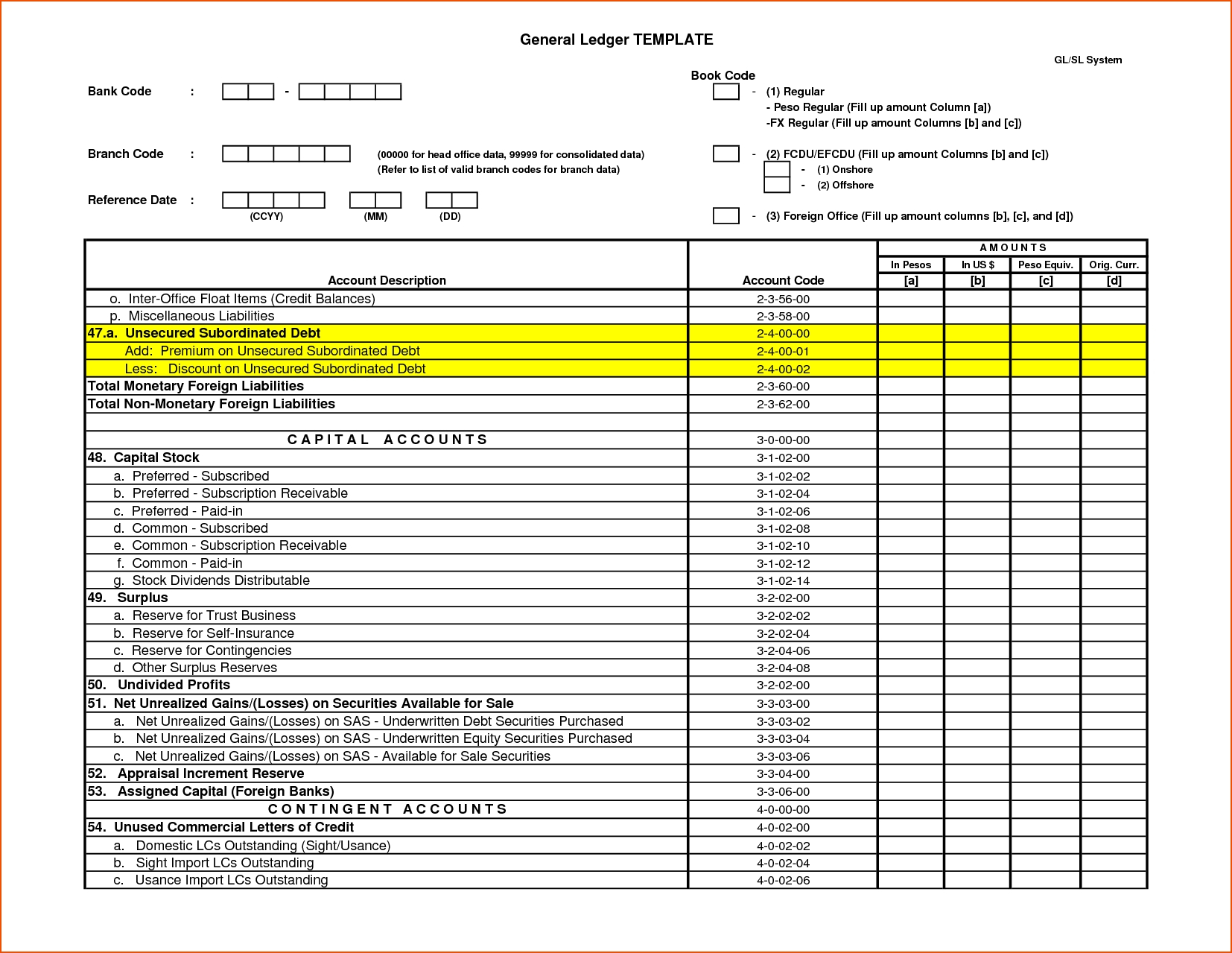
Classification of General Ledgers
Software like QuickBooks, SAP, and Oracle are commonly used to manage general ledger accounts and transactions. A subledger details transactions for specific accounts, while the general ledger summarizes all transactions across all accounts. Balancing the books used to be a demanding task, but with the helpful general ledger templates and accounting software, it is easy to automate the process, so you can focus on growing your business. It can be very difficult to organize if you have a huge number of transactions in a given accounting period, which is where GL Codes can come handy. As you can more easily find transactions you are searching for in your general ledger if you have a code for every transaction.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
So, at the beginning of the accounting period, these accounts must have a NIL balance. Reconciliation of your general ledger helps you to ensure accuracy of the information contained in your general ledger accounts. A general ledger is the second most important book of entry after the Journal, because you record transactions under specific account heads in Ledger. The assets are categorized into current assets and fixed assets, and are typically reported on the left hand side of your company’s balance sheet.
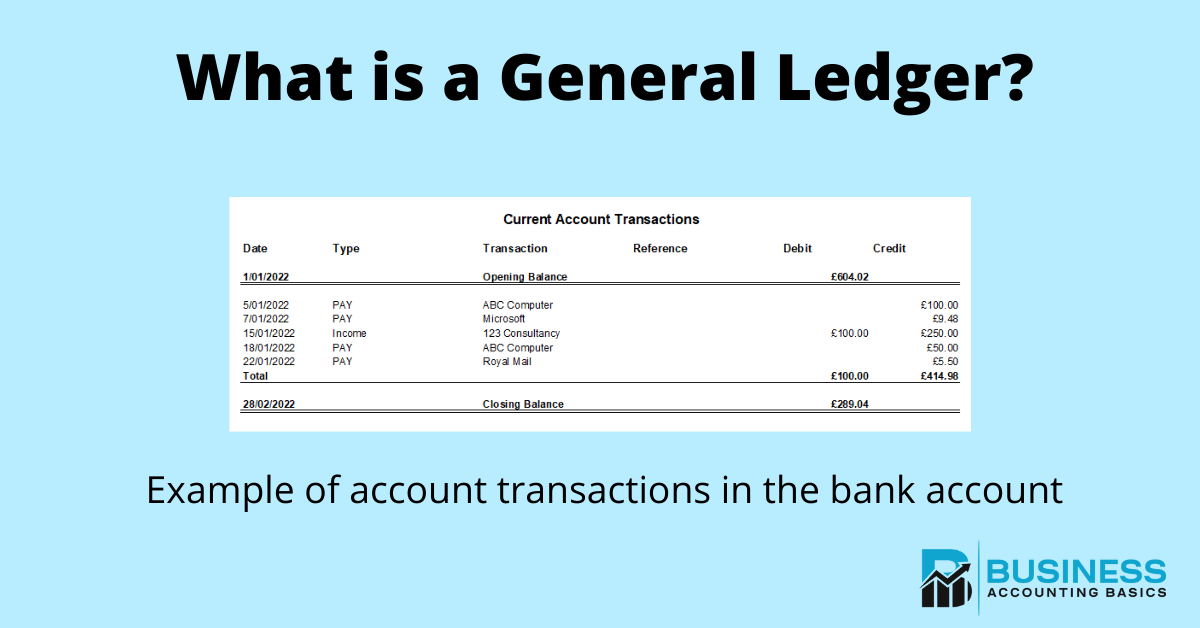
The equation remains in balance, as the equivalent increase and decrease affect one side—the asset side—of the accounting equation. General ledgers have the columns of date, description, debit and credit amount. The description could be an expense, revenue, liability, asset or equity entry. As discussed before, the financial entries are first recorded in a general journal.
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report.
If yours is inaccurate, you’ll inevitably have issues with your financial statements. On January 31, you receive a $2,500 payment for completing a project and use the cash to pay off your credit card balance. Immediately, you create the following journal entries to record the month’s transactions. Equity accounts show details in ownership interest of your business’s shareholders. Common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital are just three of the typical types of equity accounts in a GL.
You may include individual assets and accounts like accounts payable and receivable, liabilities, inventory, and investments. This information is used to prepare financial reports, monitor finances, track cash flow, and prevent accounting errors or fraud. A general ledger is an accounting record that compiles every financial transaction of a firm to provide accurate entries for financial statements. The double-entry bookkeeping requires the balance sheet to ensure that the sum of its debit side is equal to the credit side total. A general ledger helps to achieve this goal by compiling journal entries and allowing accounting calculations.
General ledger accounts are the basis on which you prepare a trial balance, from which you are able to prepare statements of final accounts, including income statements and balance sheets. Such financial statements provide information on the profitability and overall financial position of your business. You need to compare the closing trial balances of previous accounting periods to the opening balances of the current period’s ledger accounts. In doing so, you’ll need to check the balance sheet accounts for details like assets, liabilities, and stockholder’s equity. After the journal entry, the debit and credit amounts will be taken to the respective ledger accounts of cash and goods.
Tools like printable financial accounting and auditing resources help maintain and verify these records. In addition, a personal care agreement might be tracked as a specific account in the ledger, ensuring all related expenses and incomes are accounted for. Regularly generating a reconciliation statement ensures that the ledger ledger account definition is accurate and aligns with external records. This system acts as a master document detailing the business’s transactions over some time. These transactions are organized by accounts together with their dates, descriptions, and account balances—enough information to give you a bird’s-eye view of your business’s financial health.